-
Posted By admin
-
-
Comments 0
When Do Babies Start Teething: What Makes Teething Faster?
Teething is a milestone in every baby’s life — bringing excitement, curiosity, and sometimes discomfort. As parents or caregivers, you might be asking: when do babies start teething? and how can I help make this process smoother and faster for my child? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the timeline of teething, factors that influence it, proven tips to support your baby’s teething journey, and practical ways to ease discomfort.
This article is crafted for parents in the UAE seeking helpful, medically-informed guidance. We also link to our professional Pediatric Dentistry in Ajman services that provide compassionate support during your baby’s teething phase.
Understanding Teething: What is It?
Teething refers to the process of a baby’s teeth breaking through the gums. It’s a natural developmental stage, but it varies significantly from one child to another. While one baby may experience minimal discomfort, another may show noticeable fussiness.
What Happens During Teething?
When a baby’s primary teeth (also known as milk teeth) begin to erupt, the gums become swollen and sensitive. This can lead to:
- Increased drooling
- Chewing on objects
- Irritability
- Sleep disturbances
- Reduced appetite
Knowing these signs helps parents anticipate and manage the teething stage effectively.
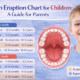
When Do Babies Start Teething? Typical Teething Timelines
One common question among caregivers is: when do babies start teething? The answer varies, but most babies begin teething around 6 months of age.
Average Teething Milestones
Age Range | Expected Teething Event |
3–4 months | Early signs may begin |
6–10 months | First primary tooth erupts (usually lower central incisors) |
9–12 months | Upper central incisors often appear |
12–18 months | Lateral incisors and first molars emerge |
18–24 months | Canines and second molars typically erupt |
By 3 years | Most children have a full set of 20 primary teeth |
It’s important to remember every baby is different. Some infants may start teething as early as 3–4 months, while others might not show signs until closer to 12 months.
Signs and Symptoms: Recognizing Teething in Your Baby
Apart from the age benchmarks, knowing when do babies start teething largely depends on recognizing the signs. These include:
Common Teething Symptoms
- Irritability and crankiness
- Excessive drooling
- Red or swollen gums
- Chewing on toys or fingers
- Mild temperature elevation (not a high fever)
- Difficulty sleeping
A 2021 pediatric review indicates that teething discomfort affects up to 70% of infants and that behavioral changes are often the most noticeable sign rather than a significant rise in temperature. (Source: Journal of Pediatric Health Care)
What Makes Teething Faster? Factors That Influence Teething Timing
While genetics largely control the timing of teething, there are practical factors that can influence how efficiently your baby progresses through this phase.
1. Genetics and Family History
Just like eye color or height, teething patterns often run in families. If you or your partner experienced early teething, there’s a good chance your baby might follow a similar timeline.
2. Nutrition Before and During Teething
Good nutrition supports healthy development, including teeth. Babies need sufficient calcium, phosphorus, and Vitamin D — typically provided by breast milk or formula in the first year.
3. Oral Muscle Development Through Chewing
Encouraging your baby to use safe teething toys or chilled items can stimulate gums and potentially aid the eruption process. The pressure helps guide the tooth as it breaks through the gum surface.
9 Ways to Support Faster & Comfortable Teething
Helping your baby through their teething stage doesn’t mean rushing the biological process, but it does mean supporting them so the experience is as smooth as possible. Here are evidence-backed strategies:
1. Use Appropriate Teething Toys
Teething toys provide safe surfaces babies can chew on. Choose BPA-free silicone or rubber toys with varying textures to help relieve gum pressure.
Tip: Keep toys chilled in the refrigerator — not frozen. Very cold items can cause gum irritation.
2. Gentle Gum Massage
Using a clean finger, gently rub your baby’s gums. This can ease discomfort and promote circulation, which may help teeth erupt sooner.
3. Offer Cold Washcloths
A clean, damp washcloth chilled in the fridge gives your baby something soft and cool to chew on. The cold helps numb the gums and offer relief.
4. Balanced Nutrition
For older babies (6+ months), introducing foods like mashed avocado or chilled pureed fruits can be soothing. Nutrient-rich foods support strong tooth and bone development.
5. Breastfeeding Comfort
Breastfeeding provides not just nutrition but also comfort. The sucking motion may soothe aching gums and reduce stress for your baby.
6. Maintain Oral Hygiene
Wiping gums with a soft cloth after feedings helps keep the mouth clean and may reduce irritation. As teeth emerge, begin brushing with a soft infant toothbrush.
7. Teething Gels: Use with Caution
Some teething gels provide topical relief. Always consult a pediatrician before use and prefer products approved for infants.
8. Distraction and Comfort
Cuddling, gentle rocking, or singing can soothe a distressed baby. Emotional comfort helps lower overall discomfort linked to teething.
9. Consult a Pediatric Dentist
If teething behaviors seem extreme or your baby exhibits high fever, diarrhea, or unusual symptoms, seek professional care. Our Pediatric Dentistry in Ajman team can evaluate concerns and offer tailored support.
What Not to Do: Avoid These Teething “Remedies”
Certain home remedies are not recommended:
- Amber teething necklaces: Risk of choking and no proven benefit.
- Frozen items: Can be too cold and damage delicate gum tissue.
- Adult pain relievers without pediatric guidance: May be harmful unless prescribed.
Always consult a healthcare provider when in doubt.
When to Call the Doctor
Teething is a normal process, but if your baby shows any of the following, contact a pediatric professional:
- High fever (above 38°C / 100.4°F)
- Persistent diarrhea or vomiting
- Severe lethargy
- Gum infections or pus
- Signs of dehydration
In such cases, a pediatric examination can rule out infections or other causes of discomfort.
Real Parent Tips: What Worked for Others
Many parents find success with a combination of chilled teething rings, distraction play, and consistent routines. One mother shared:
“Giving my baby a chilled silicone ring and extra cuddle time made a world of difference. She seemed calmer and started smiling more even while teething!”
These personal stories illustrate that comfort, consistency, and patience are key.
Key Takeaways
- Most babies begin teething around 6 months, but individual timelines vary.
- Teething symptoms include irritability, drooling, and chewing on objects.
- Genetics, nutrition, and gum stimulation influence teething progress.
- Safe teething toys, gum massage, and chilled items can soothe your baby.
- Avoid unsafe practices like amber necklaces or unprescribed medication.
- Consult pediatric professionals if symptoms are severe or unusual.
As you support your baby through this journey, remember that patience and love go a long way. Every milestone — including tooth eruption — is a step toward a happy, healthy childhood.
FAQs
What age do babies typically start teething?
Most babies begin teething around 6 months of age, although some may start earlier (around 3–4 months) or later (up to 12 months). The first teeth to appear are typically the lower central incisors.
How can I tell if teething is causing fussiness?
Signs include drooling, chewing on objects, swollen gums, and mild irritability. While some discomfort is normal, high fever or severe symptoms should be evaluated by a pediatric provider.
Are there safe ways to make teething faster or easier?
Teething can’t be rushed, but you can support your baby with chilled teething toys, gentle gum massage, balanced nutrition, and distraction techniques to ease discomfort and encourage progress.
When do I need to seek medical help for teething issues?
Contact a pediatrician if your baby has a high fever, persistent diarrhea, unusual lethargy, or signs of infection. Professional evaluation ensures that other health issues are not mistaken for teething.
What role does nutrition play in teething?
Good nutrition supports overall development, including dental health. For infants, breast milk or formula provides essential nutrients; for older babies, introducing iron-rich, soft foods after 6 months helps support growth and comfort during teething.