-
Posted By admin
-
-
Comments 0
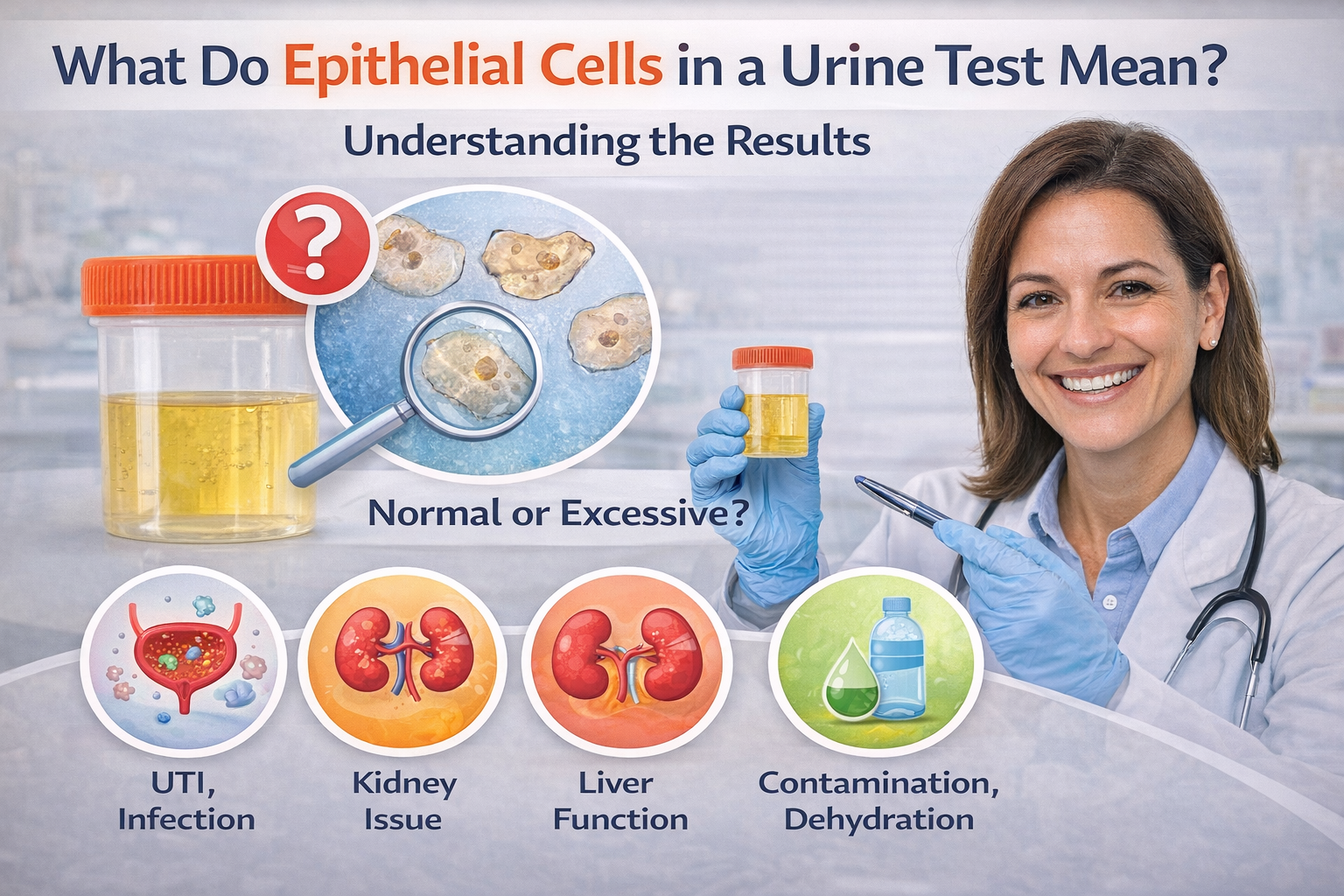
What Do Epithelial Cells in a Urine Test Mean? Understanding the Results
Urine tests are among the most commonly ordered diagnostic tools in healthcare. One parameter that often catches a patient’s attention is the presence of epithelial cells. But what does this mean for your health? Is it something to worry about?
This guide will break down what urine test epithelial cells are, when they are normal or abnormal, and what conditions they may indicate particularly for residents of Ajman, Dubai, and nearby UAE regions seeking quality healthcare solutions.
What Are Epithelial Cells?
Epithelial cells line surfaces throughout the body, including the urinary tract. These cells naturally shed and may appear in small amounts in your urine. There are three main types:
- Squamous epithelial cells – from the outer urethra
- Transitional epithelial cells – from the bladder or upper urethra
- Renal tubular epithelial cells – from the kidneys (least common, more concerning)
A few cells in your urine are usually harmless. However, a high count of epithelial cells could indicate infection, inflammation, or kidney issues.
Why Are Epithelial Cells Measured in a Urine Test?
The urine test epithelial cells count is part of a standard urinalysis, which helps detect urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney conditions, or contamination in the sample.
Epithelial Cell Types and Their Implications
|
Type of Epithelial Cell |
Possible Origin |
Health Implication |
|
Squamous |
Lower urethra or skin |
Often due to contamination |
|
Transitional |
Bladder, upper urethra |
May indicate UTI or inflammation |
|
Renal Tubular |
Kidney |
Possible sign of kidney damage/disease |
What Does a High Epithelial Cell Count Indicate?
If your lab report shows urine test epithelial cells in high numbers, your doctor will consider:
- Contamination during sample collection (especially squamous cells)
- Urinary tract infections
- Kidney disorders (renal tubular epithelial cells)
Bladder inflammation or irritation
In many cases, repeat testing or further diagnostic tools like a urine culture or blood tests may be advised for accuracy.
How Do Doctors Interpret the Results?
A lab technician or your physician will look at the number and type of epithelial cells, combined with other elements like:
- White blood cells
- Red blood cells
- Bacteria
- Protein levels
These combined readings help determine whether further investigation is needed. If renal tubular epithelial cells are present, it often triggers concern regarding kidney health and may prompt tests like creatinine, GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate), or imaging studies.
Symptoms That May Appear with Abnormal Results
While epithelial cells themselves don’t cause symptoms, conditions they indicate often do. Be alert for:
- Frequent or painful urination
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- Lower back or side pain
- Fever (especially in UTIs)
- Swelling in legs or ankles (kidney-related)
If you notice these signs, it’s advisable to consult a physician for further evaluation.
When to Seek Medical Attention in Ajman
For patients in Ajman or Dubai experiencing persistent urinary symptoms or abnormal urine results, a consultation with a local clinic is vital. Urine infection treatment Ajman services at Amtek Medical offer walk-in diagnosis, lab tests, and doctor-guided treatment to address your concerns promptly.
Key Takeaways
- A small number of epithelial cells in a urine sample is normal.
- High levels may suggest contamination, urinary infections, or kidney disease.
- Identifying the type of epithelial cell (squamous, transitional, renal) helps narrow down potential causes.
- Further testing and clinical correlation are essential before diagnosing any underlying issue.
- If you experience urinary symptoms, don’t ignore them—early intervention ensures better outcomes.
FAQs
1. Are epithelial cells in a urine test dangerous?
Not always. A small number is typically harmless, but elevated levels could point to infection or kidney problems, especially if renal cells are involved.
2. Can I prevent high epithelial cell levels in my urine?
Good hygiene, staying hydrated, and promptly treating urinary symptoms can help prevent infections that may raise epithelial cell counts.
3. Do I need treatment if epithelial cells are found in my urine?
If found in high quantities, your doctor may investigate further. Treatment depends on whether there’s an underlying infection or kidney issue.
4. What causes renal tubular epithelial cells in the urine?
These can be a sign of kidney injury, damage due to infections, medications, or other conditions like glomerulonephritis.
5. Is it possible to have epithelial cells in urine without symptoms?
Yes, especially if it’s due to sample contamination. That’s why clinical context and additional tests are crucial for diagnosis.
Final Thoughts
Understanding your urine test epithelial cells result can feel overwhelming, but it’s a critical clue your body provides. If you’re unsure about your results or experiencing discomfort, visit a trusted clinic in Ajman or Dubai. At Amtek Medical, we prioritize accurate diagnostics and personalized care to keep your urinary health in check.


