-
Posted By admin
-
-
Comments 0
Teeth Calcium Deficiency Treatments: Causes and How to Treat It
Calcium plays a vital role in maintaining strong and healthy teeth. When your body lacks sufficient calcium, the effects can manifest in various parts of your body—especially your oral health. Teeth calcium deficiency is a common issue affecting many individuals, often silently undermining dental integrity until symptoms become severe. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available teeth calcium deficiency treatments is crucial to preserving not just your smile, but your overall well-being.
In this blog, we will explore the key reasons behind calcium deficiency in teeth, how to identify its signs early, and effective methods to treat and prevent it.
What is Teeth Calcium Deficiency?
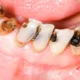
Teeth calcium deficiency, also known as hypocalcification, occurs when the enamel (the protective outer layer of your teeth) is inadequately mineralized. This condition weakens your teeth, making them more susceptible to decay, cavities, and gum disease.
While calcium is predominantly stored in bones and teeth, a deficiency often results from inadequate intake, poor absorption, or accelerated loss of calcium due to underlying health conditions.
Common Causes of Teeth Calcium Deficiency
Calcium deficiency in teeth may result from various lifestyle, dietary, and medical factors. Below are the most prevalent causes:
1. Poor Dietary Intake
- Inadequate consumption of calcium-rich foods like dairy products, leafy greens, almonds, and fortified cereals.
- Vegan or dairy-free diets without proper supplementation.
2. Vitamin D Deficiency
- Vitamin D helps your body absorb calcium efficiently.
- A lack of sunlight exposure or low dietary intake can impair this process.
3. Medical Conditions
- Hypoparathyroidism: Reduced production of parathyroid hormone leads to low calcium levels.
- Kidney Disease: Impairs calcium-phosphorus balance and vitamin D metabolism.
- Celiac Disease: Damaged intestinal lining reduces calcium absorption.
4. Hormonal Changes
- Women undergoing menopause often experience calcium loss due to decreased estrogen levels.
5. Genetics
- Enamel hypoplasia is a hereditary condition where teeth form with inadequate enamel.
Symptoms of Calcium Deficiency in Teeth
Early identification of symptoms can help in timely intervention. Look out for the following signs:
- Increased tooth sensitivity
- White spots or discoloration on teeth
- Frequent cavities or decay
- Weak, brittle, or chipped teeth
- Gum inflammation and bleeding
- Bad breath
If you observe any of these symptoms, consult a dental professional immediately for evaluation and guidance.
Effective Teeth Calcium Deficiency Treatments
Treating calcium deficiency involves a multi-dimensional approach: improving diet, managing underlying medical conditions, and employing dental procedures when necessary. Here’s a breakdown of proven teeth calcium deficiency treatments:
1. Nutritional Supplementation
A balanced intake of calcium is the foundation for healthy teeth. Adults typically require 1000–1300 mg of calcium daily, depending on age and gender. Supplements can be recommended when dietary sources fall short.
Include in your diet:
- Dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt)
- Leafy greens (kale, spinach)
- Fortified plant-based milk (almond, soy)
- Nuts and seeds (chia, sesame, almonds)
- Fatty fish (salmon, sardines with bones)
Also, don’t forget vitamin D for effective calcium absorption. Sun exposure and foods like egg yolks and fish oils can help.
2. Topical Fluoride Treatments
Topical fluoride can strengthen weakened enamel and prevent further decay. Dentists may apply concentrated fluoride varnishes or gels to improve tooth resistance.
3. Remineralization Therapies
These treatments are aimed at restoring lost minerals to enamel using calcium and phosphate-rich pastes. Casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate (CPP-ACP) products are particularly effective.
4. Dental Sealants and Fillings
For teeth already affected by cavities due to calcium deficiency, dental fillings or sealants can restore structure and function. Sealants prevent decay in grooves and crevices of molars.
5. Scaling and Cleaning
Plaque buildup exacerbates enamel erosion and weakens calcium-deficient teeth. Professional dental cleaning and teeth scaling Ajman can significantly reduce bacterial load, ensuring better oral hygiene and preventing further mineral loss.
6. Hormonal and Medical Management
In cases linked to hormonal imbalances or chronic illnesses:
- Manage underlying conditions with the help of endocrinologists or general physicians.
- Treat conditions like kidney disease, thyroid dysfunction, or gastrointestinal issues to support calcium absorption.
Preventing Teeth Calcium Deficiency: Proactive Measures
While treatment is essential, prevention is even better. Consider these daily habits to safeguard your dental health:
- Brush with fluoride toothpaste twice daily
- Floss to remove plaque between teeth
- Eat a calcium-rich, balanced diet
- Avoid sugary and acidic foods that weaken enamel
- Regular dental check-ups every six months
- Stay hydrated to aid remineralization via saliva
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol—both impair calcium metabolism
Comparison Table: Treatments vs Benefits
|
Treatment Method |
Primary Benefit |
Ideal For |
|
Calcium Supplements |
Restores mineral balance |
General deficiency cases |
|
Fluoride Applications |
Strengthens enamel |
Early enamel weakening |
|
Remineralization Products |
Rebuilds tooth minerals |
White spots, mild demineralization |
|
Dental Sealants/Fillings |
Restores structure, prevents decay |
Cavities, erosion |
|
Professional Scaling |
Eliminates plaque, promotes hygiene |
Preventive and ongoing care |
FAQs
1. Can children also suffer from teeth calcium deficiency?
Yes, children are especially vulnerable due to their developing teeth and bones. Ensuring they consume adequate calcium and vitamin D is crucial.
2. How long does it take to reverse calcium deficiency in teeth?
It varies by individual. With proper nutrition and dental care, improvement may be seen in weeks, but restoring enamel strength can take several months.
3. Are dairy-free alternatives effective for calcium intake?
Yes, many plant-based milks are fortified with calcium and vitamin D. Always check labels to ensure adequate supplementation.
4. Can I treat calcium deficiency at home without a dentist?
While you can support oral health with diet and supplements, professional evaluation is necessary to assess the extent of enamel damage and recommend personalized treatments.
5. Is there a connection between teeth sensitivity and calcium levels?
Absolutely. Calcium-deficient enamel offers less protection, exposing dentin and causing increased sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet stimuli.
Final Thoughts
Maintaining optimal calcium levels is a foundational element of oral health. By recognizing the symptoms early and adopting a proactive approach that includes dietary, lifestyle, and professional treatments, you can effectively combat and prevent teeth calcium deficiency.
If you suspect early signs of dental calcium loss or just want to ensure your oral hygiene is on point, consider scheduling a professional cleaning or teeth scaling in Ajman today.
Your smile deserves nothing but the best.